This water-soluble vitamin plays a major role in the formation of red blood cells, synthesis of DNA, and nerve functioning within the body. Among all the benefits it has, vitamin B12 and brain function are highly important, as this nutrient directly influences memory, mood, and cognitive performance.
Because of its importance, it is of great importance to understand how this vitamin maintains mental health and why its sufficiency is so crucial. Let us explore the benefit of Vitamin B12 for brain function and overall well-being.
What is Vitamin B12?
Vitamin B12 is a water-soluble vitamin found in different animal-related foods, including meat fis,h, and even dairy products; it is essential for your body.
However, these cannot be synthesized by your body; hence, the consumption of such through diet or supplements becomes a requirement. Physiologically, the benefit of vitamin b12 and Vitamin B12 works by offering energy to maintain nerve health and support cognitive function.
According to Dr Rita, an anatomy specialist, apart from serving as an energy booster, vitamin b12 for brain health protects your nervous system. One of the distinctive roles played by vitamin b12 and brain health is involvement in myelin production and protective sheath of nerves, without which there would be no smooth transmission of impulses between the brain and the body. This vitamin supports neurotransmitter synthesis, which is important in mood and cognition.
The dietary sources of vitamin B12 for brain health include fish, poultry, eggs, and fortified cereals. For those on restricted diets, such as vegans or vegetarians, supplementation becomes necessary to avoid deficiency.
The Link Between Vitamin B12 and Brain Health
Vitamin B12’s function in the body is highly vital for brain health and, generally for cognitive activity. It plays an important role in the proper functioning of the brain and protects it from damage due to deficiency.
People do not usually realize how much their clear-headedness, concentration, and even mood are dependent on an adequate level of vitamin B12. Without this, the brain could have a variety of problems, some of which are serious and can even be permanent.
One of the important roles of vitamin B12 in the brain is myelin synthesis. Myelin acts like an insulator for your nerves, which helps them conduct properly and faster.
If your levels of vitamin b12 for brain function are too low, the production of myelin will be impaired, which reduces the speed of nerve impulses and impairs communications between nerve cells. This may manifest in the form of forgetfulness, confusion, or the inability to think clearly.
The more this deficiency persists, the graver the nerve damage will be to contribute to dementia or other neurological diseases. It goes to show that vitamin b12 is fairly important for brain health in terms of the well-being of the brain and its optimal performance.
Vitamin B12 benefits the brain, but it also plays a huge role in neurotransmitter creation: the chemical messengers the brain uses to talk to itself and other parts of the body.
The two major neurotransmitters most influenced by vitamin B12 are serotonin and dopamine. These neurotransmitter chemicals are very important in managing mood, mind concentration, and general mental balance.
A deficiency in vitamin B12 can make any person sad, irritable, and depressed, and cognitive performance can come down drastically. In these cases, the role of vitamin B12 in the functioning of the brain is very evident, and its role in keeping the mind healthy is proved beyond doubt.
Key Benefits of Vitamin B12 for the Brain
Enhances Cognitive Ability
One of the most significant vitamin B12 benefits for the brain is increasing cognitive function and improving memory, concentration, and clarity. Indeed, studies have confirmed that adequate B12 levels support the prevention of memory loss among older adults. Vitamin B12 improves brain function and mental clarity since it supports the production of myelin and is good for nerve health.
Prevents Neurological Disorders
A deficiency in vitamin B12 affects brain health and has dire consequences for severe neurological disorders, such as dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. There is evidence from different studies that sufficiency of B12 reduces disorders in the dementing state of a person, and Alzheimer’s disease again reflects how vital vitamin B12 is and its association with the human brain.
Supports Mood Regulation
Mood swings and symptoms of depression are related to low levels of Vitamin B12. It plays a role in the synthesis of neurotransmitters involved in controlling mood, serotonin, and dopamine. Supplementing with vitamin B12 for focus and emotional stability may reduce symptoms of depression in people who lack the vitamin. If you’re looking for the best dopamine supplements, consider adding Vitamin B12 to your routine for a boost in mood and mental clarity.
Reduces Brain Fog and Fatigue
Brain fog caused by B12 deficiency may take manifestations of confusion and fogginess with reduced mental clearheadedness. However, high-sufficiently higher levels of Vitamin B12 in the body fight it with healthy red blood cells that go straight to providing well-oxygenated blood, consequently reducing fatigue for enhancing focus and good concentration of a person in this regard.
Signs of Vitamin B12 Deficiency and Its Impact on the Brain
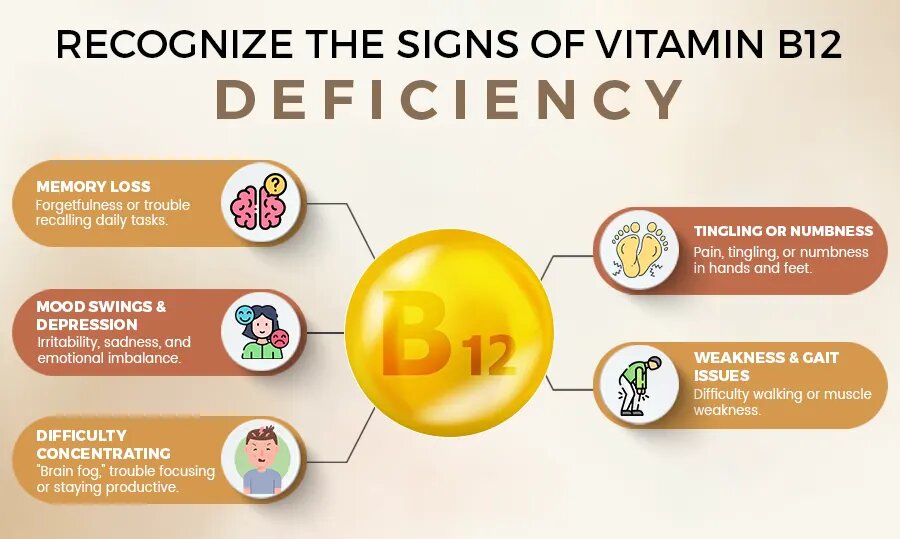 Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Vitamin B12 DeficiencyA lack of vitamin b12 for brain function can have serious implications for mental health and cognitive performance.
Vitamin B12 is very important to the brain and nervous system; thus, a deficiency can cause disturbances in many processes critical for clear thinking, emotional balance, and nerve function. Recognizing the signs of a vitamin B12 deficiency early is essential to prevent long-term damage.
Common Symptoms of Vitamin B12 Deficiency:
- Memory Loss: A lack of vitamin B12 can make it difficult for the brain to store and retrieve information. It usually presents as forgetfulness or inability to recall the details of daily life, even the simplest tasks. Memory lapses due to deficiency of vitamin B12 worsen with time if not treated and may lead to diseases such as dementia.
- Difficulty Concentrating: Vitamin B12 is another very important factor to focus on, as it supports nerve function and energy production, hence sustaining concentration over a long period. Generally, people with low levels of B12 have problems with keeping attention, being productive, or focusing on something. This mental fogginess, sometimes referred to as “brain fog,” can make even routine activities feel overwhelming.
- Mood Swings or Depression: The lack of vitamin B12 disrupts the synthesis of two neurotransmitters, carriers of mood maintenance: serotonin and dopamine. It may cause mood swings, irritability, or just a continuous state of sadness. Some people with low levels of vitamin B12 may develop clinical depression because their brain is not capable of sustaining emotional balance.
- Neuropathy: tingling, numbness, or pain in your hands and feet caused by nerve damage.
- Severe Cognitive Decline: Chronic deficiency of vitamin B12 and brain maladies may eventually rise to as bad as Alzheimer’s disease or another form of dementia.
- Impaired Motor Function: Difficulty in walking, gait disturbances, or weakness of the muscles, which is directly linked to some nerve damage.
Long-Term Effects of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
A long-term deficiency in vitamin B12 can result in permanent neurological damage. The brain and spinal cord can deteriorate nerves because of a lack of myelin, the fatty substance that surrounds and protects nerve fibers. This may cause irreversible problems to include the following:
Early Detection and Intervention
Early recognition of symptoms is thus crucial to avoid these serious sequelae. It is relatively easy to measure B12 levels in the blood, and screening can highlight if an individual has a risk.
Treatment usually involves dietary changes or supplementation with vitamin b12 for brain function through oral tablets or injections.
The deficiency, if treated early, is reversible, and many of the symptoms, especially if the deficiency and symptoms are treated early, disappear.
It often takes weeks to see significant improvements in memory, focus, and even mood after increasing intakes of vitamin b12 for focus. In the case of more serious neurological damage, intervention can often prevent further deterioration and assist in symptom management.
How to Ensure Adequate Vitamin B12 Intake
To derive proper benefits from Vitamin B12, one needs to maintain its consumption either through diet or supplementation. Here are ways you could ensure your body gets enough of this important nutrient.
Dietary Sources Foods that naturally offer vitamin B12 for brain health of a person include:
- Meats: Beef, pork, and liver are excellent sources.
- Fish: Salmon, tuna, and trout have high amounts of B12
- Dairy Products: Milk, Cheese, and yogurt are rich in the vitamin.
- Fortified Foods: Cereals and plant-based milk that have been fortified with B12 are very good options for vegans and vegetarians.
Supplements
If the diet is found to be inadequate in this regard, supplements are there. Oral tablets, sublingual forms, and injections may work effectively in boosting the functions of vitamin B12 within the body. Consult a health expert for advice on what may be best for you.
Recommended Daily Intake
The recommended daily intake for most adults is 2.4 micrograms, although there is a need for higher amounts in pregnant or lactating conditions. It requires regular intake to allow for vitamin B12’s effects on brain health.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does Vitamin B12 support brain function?
Vitamin B12 is involved in the production of myelin, the synthesis of neurotransmitters, and maintains effective nerve communication. All these functions are necessary to maintain mental clarity and concentration.
What does a lack of B12 do to the brain?
This can cause one to have forgetfulness, poor concentration, and mood swings. Long-term damage can lead to nerve damage and cognitive decline, which is irreparable.
Can B12 supplements improve focus and memory?
Yes, most especially in the deficient ones. The right level of vitamin B12 to maintain focus enhances one’s memory, concentration, and overall cognitive functioning.
Who has the greatest risk of Vitamin B12 deficiency?
Older adults, vegans, vegetarians, and people who have problems with absorption are the ones at risk. Certain medical conditions, like pernicious anemia and disorders in the digestive system, affect B12 absorption.
Does B12 help with brain fog?
Yes, Vitamin B12 supports nerve function, oxygen delivery, and cognitive processes, all of which help reduce brain fog. Adequate B12 levels improve clarity, focus, and memory retention.
Does B12 increase dopamine?
Yes, Vitamin B12 plays a role in the synthesis of dopamine, a neurotransmitter essential for motivation, focus, and emotional regulation. Low B12 levels may contribute to mood disorders and cognitive decline.
Conclusion
Vitamin B12 is crucial for mental clarity, mood stability, and cognitive performance. Its ability to form myelin, facilitate neurotransmitter synthesis, and boost memory and focus underlines vitamin B12’s very important role in the brain.
With sufficient intake through diet or supplementation, one can reap all the vitamin B12 benefits that ensure brain health and prevent neurological disorders for overall wellness.
If you’re experiencing symptoms like memory loss, brain fog, or fatigue, consider assessing your B12 levels. Consult a healthcare provider to determine if supplementation is necessary.
Maintaining optimal levels of vitamin B12 is good for brain function, mood regulation, and energy production. Take steps today to prioritize your brain health and harness the full benefit of vitamin B12 for a sharper, healthier mind.

